

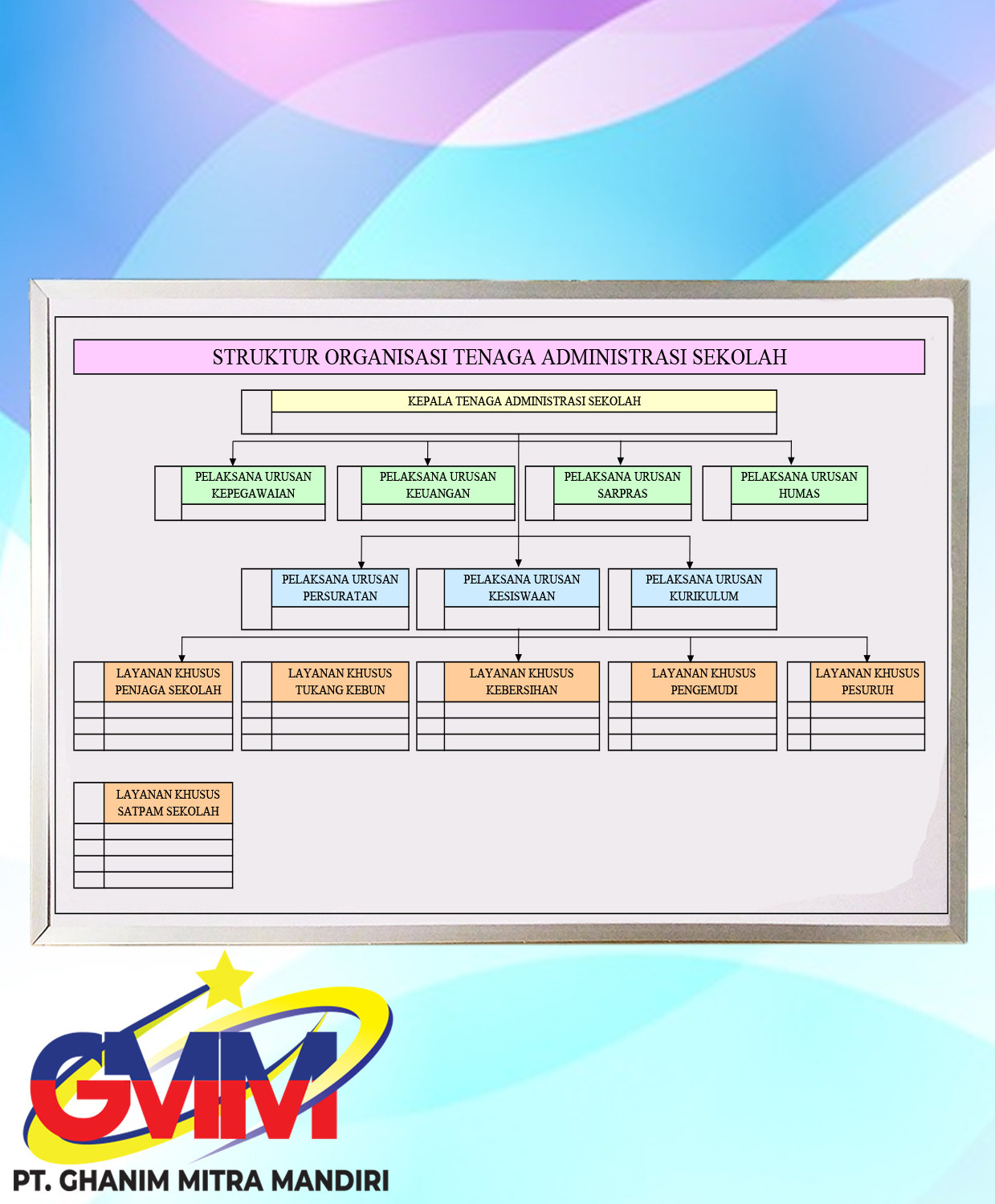
Databases are not used only to hold administrative information, but are often embedded within applications to hold more specialized data: for example engineering data or economic models. Increasingly, databases are not only used to support the internal operations of the organization, but also to underpin its online interactions with customers and suppliers (see Enterprise software). Most organizations in developed countries today depend on databases for their business operations. This article is concerned only with databases where the size and usage requirements necessitate use of a database management system. Outside the world of professional information technology, the term database is sometimes used casually to refer to any collection of data (perhaps a spreadsheet, maybe even a card index). The term database system implies that the data is managed to some level of quality (measured in terms of accuracy, availability, usability, and resilience). Collectively, they can be called a database system.
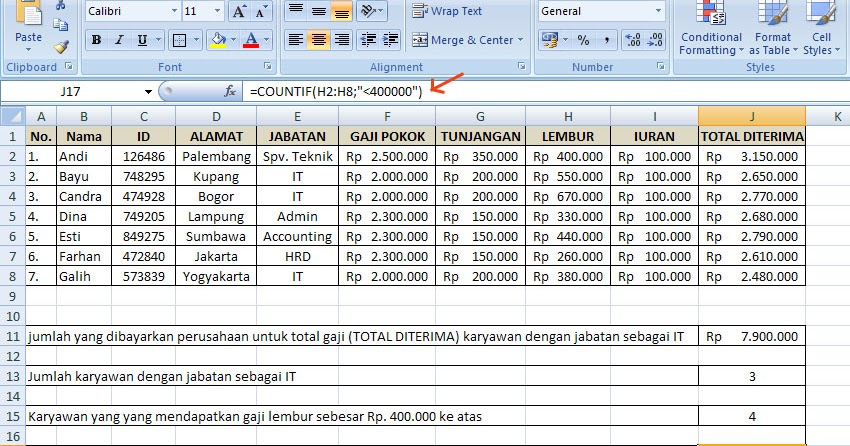
2.1 General-purpose and special-purpose DBMSs.A database is not generally portable across different DBMS, but different DBMSs can inter-operate by using standards such as SQL and ODBC or JDBC to allow a single application to work with more than one database. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Oracle, Sybase, FoxPro, and IBM DB2. Personal, desktop-based database systems have less complexity. The complexity of a client-server or transactional DBMS arises because of the need to maintain high performance, availability and security when many users are querying and updating the database at the same time. The data is typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality (for example, the availability of rooms in hotels), in a way that supports processes requiring this information (for example, finding a hotel with vacancies).Ī general-purpose database management system (DBMS) is a software system designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases, which are often large and complex. A database is an organized collection of data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
